Introduction
The .htaccess file is one of the most powerful tools in your WordPress arsenal. Standing for “hypertext access,” this configuration file tells your server how to handle specific tasks like redirects, security, and the “pretty” permalinks that make your URLs look professional. It gives you the ability to modify every functionality of your site.
However, because it is a “dotfile” (a hidden file), it can be elusive for beginners. At Gotmyhost, we believe in empowering our users with the right knowledge. In this guide, we’ll show you exactly how to find, create, and safely edit your .htaccess file.
What Exactly is the .htaccess File?
Think of the .htaccess file as a gatekeeper for your server. It lives in your site’s root directory and processes requests before they even reach WordPress. It allows you to:
- Set up 301 redirects.
- Password-protect specific folders.
- Improve site security by blocking specific IP addresses.
- Enable caching to speed up your site.
Phase 1: How to Locate Your Default .htaccess File
By default, the .htaccess file is hidden. If you open your site files and don’t see it, it’s likely because your file manager is set to hide “dotfiles.”
There are two methods of locating it. One is using cPanel, and the other is with an FTP client software program. Here are both the ways below:
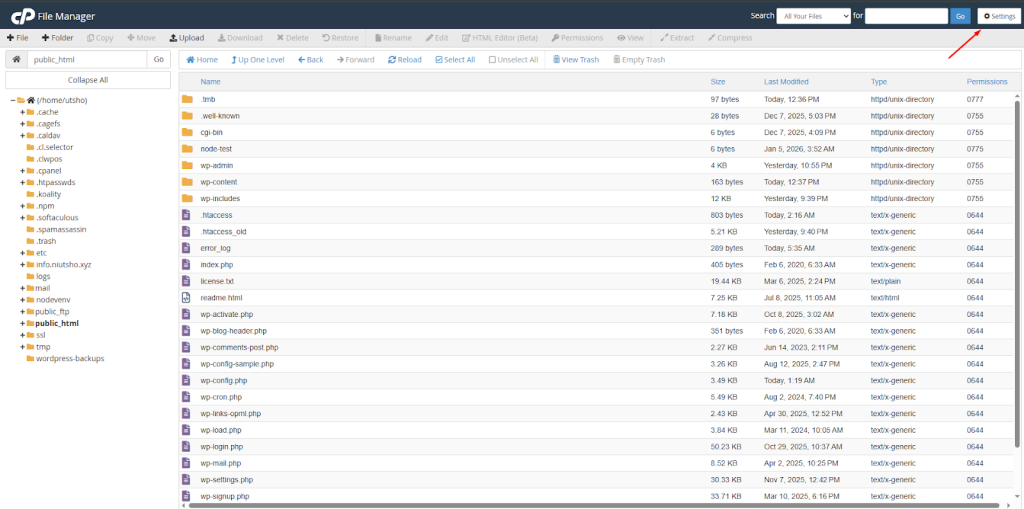
Method A: Using Gotmyhost File Manager (cPanel)
- Log in to your Gotmyhost cPanel.
- Open the File Manager.
- Go to the public_html folder.
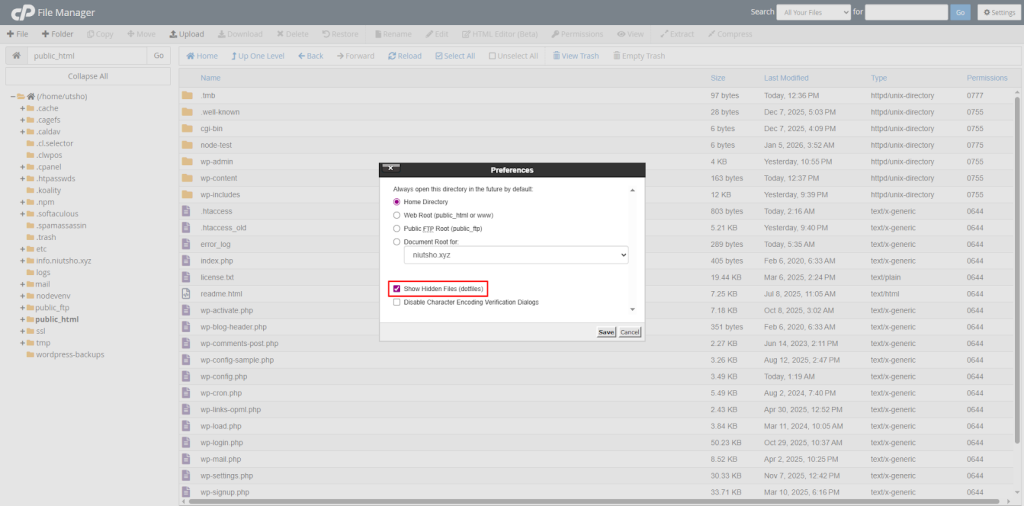
- Click Settings in the top right corner.
- Check the box for “Show Hidden Files (dotfiles)” and click Save.
- The .htaccess file should now appear in the list.
Method B: Using FTP (FileZilla)
FTP clients are just software that help transfer files between the local and remote server. You can use FTP software like FileZilla, Cyberduck, or WinSCP to locate the file. Here are the steps:
Step 1: First, download and install an FTP client software like FileZilla, Cyberduck, or any other you like.
Step 2: Configure your web server settings by entering the host, port, login type, username, and password. You’ll get these from your web server’s control panel.
Step 3: Open your FTP client and navigate to the root directory of your WordPress installation. This is usually the “public_html” folder or a folder with the name of your website.
Step 4: Look for the .htaccess file in the directory. If you can’t see it, make sure that you have enabled the option to show hidden files and folders in your FTP client.
Phase 2: How to Create a .htaccess File (If It’s Missing)
Sometimes, the file simply doesn’t exist. This often happens on fresh installations or if it was accidentally deleted.
The “Permalinks” Shortcut
The easiest way to force WordPress to generate a new .htaccess file is through the dashboard:
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks.
- Do not change any settings.
- Scroll down and click “Save Changes”.
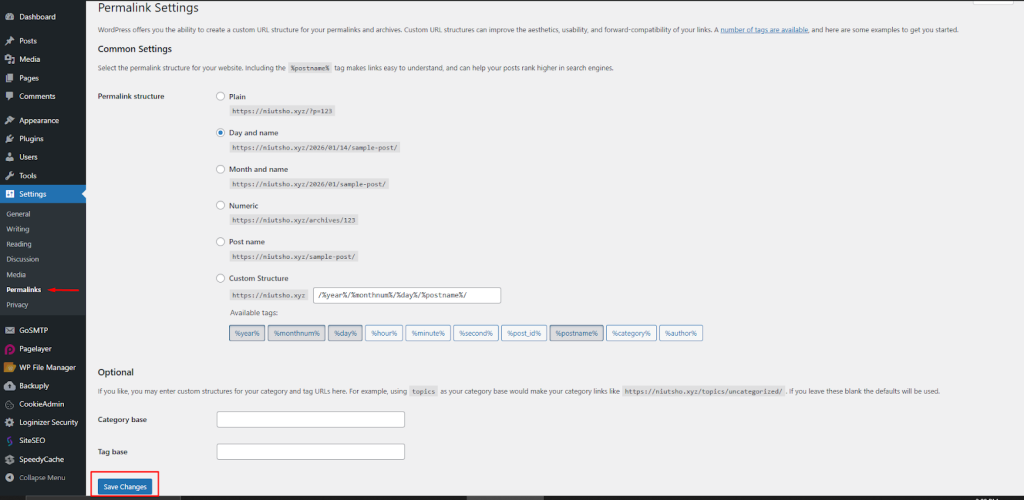
- WordPress will automatically try to create a new file in your root directory.
The Manual Method :
If the shortcut fails, you can create it manually. The best way to have your default .htaccess file is by creating it right within the root directory. Here are the
steps to do it:
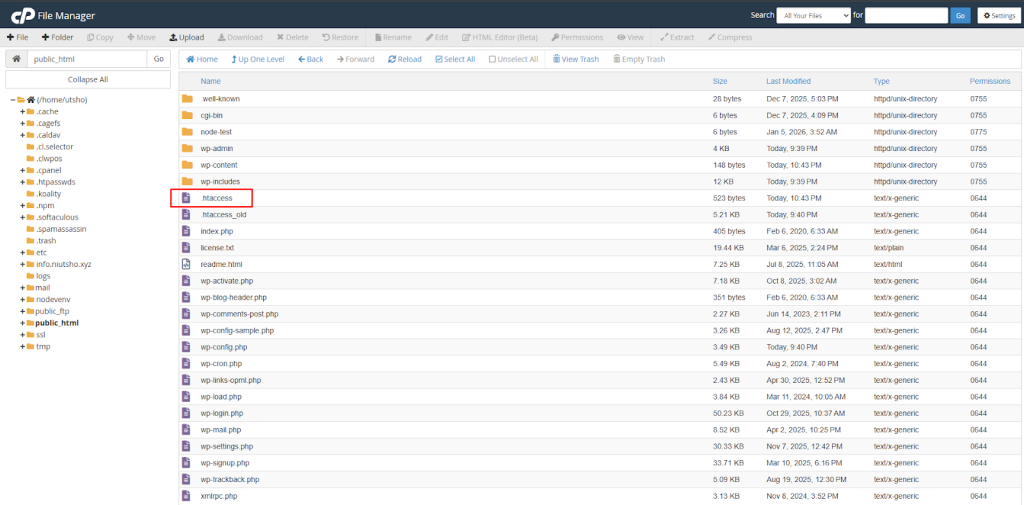
Step 1: Navigate to the root directory following the method described above.
Step 2: Click on the “+File” Button to add/create a new file within the root folder.
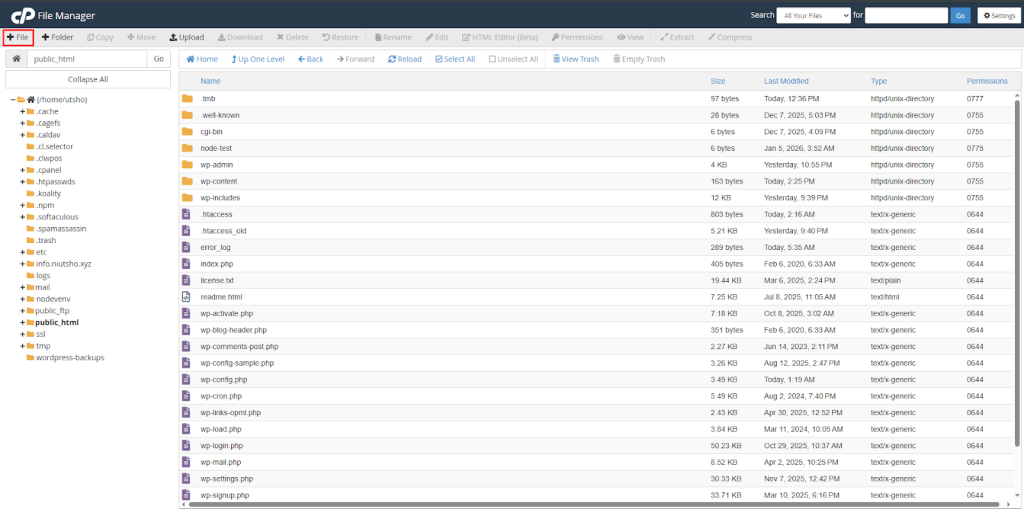
Step 3: Write .htaccess as the file name and press enter to see a text editing field.
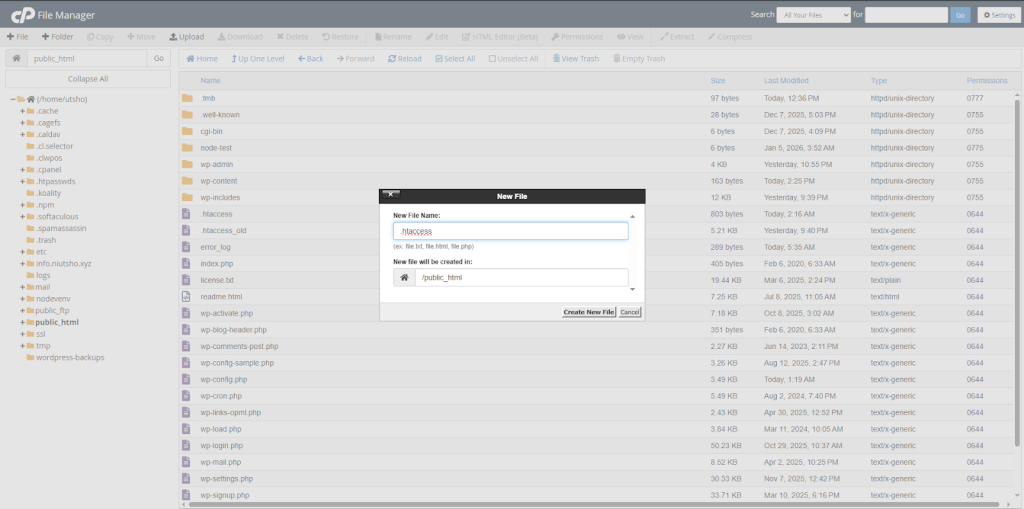
Step 4: In the text field, copy and paste the code below, save the file, and you’ll have your default .htaccess file.
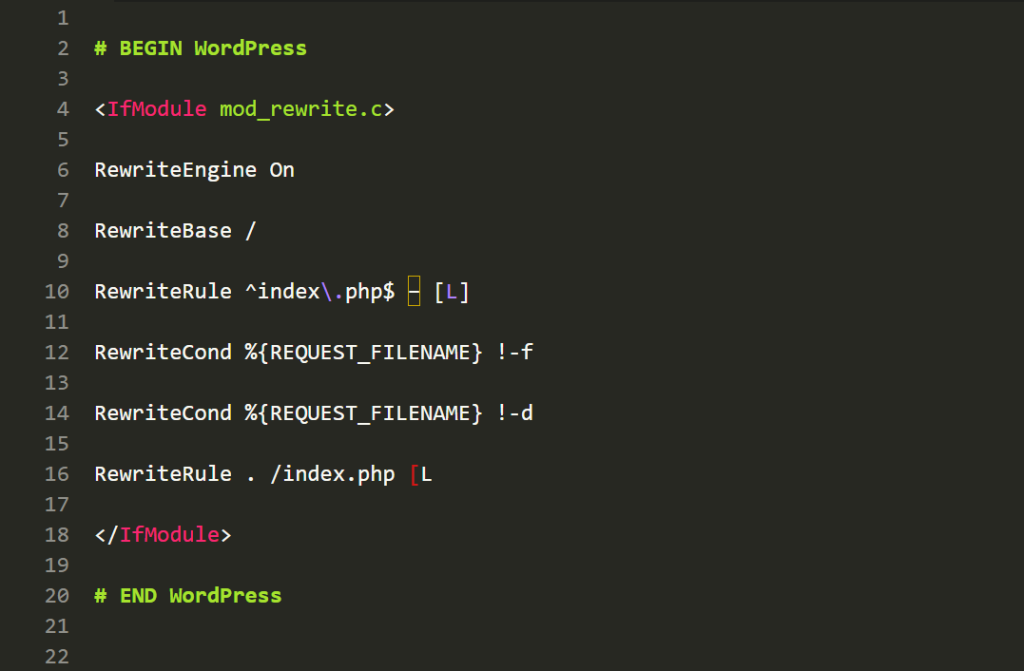
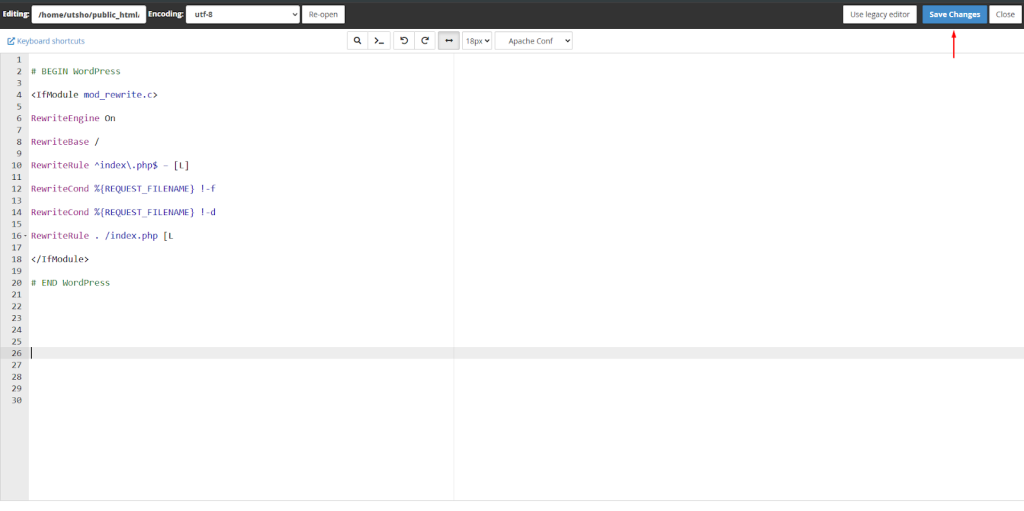
Note: If your file is empty or corrupted, you should restore it to the standard WordPress configuration. Copy and paste this exact code. Always place your custom code above the # BEGIN WordPress line or below the # END WordPress line. Anything inside those brackets can be overwritten by WordPress updates.
Phase 3: How to Edit the File Safely
Editing the .htaccess file is high-stakes. A single misplaced character can trigger a 500 Internal Server Error, making your site inaccessible.
Follow these professional rules:
- Backup first: Always download a copy of the current file to your computer before editing.
- Use a Text Editor: Never use Word or Google Docs. Use the built-in cPanel editor or a code editor like Notepad++ or VS Code.
- One change at a time: Add one rule, save, and refresh your site to ensure it still works.
The .htaccess file is a configuration document for use in WordPress websites. This file plays an important role in keeping your site accessible, as it determines how the server runs and functions. Every WordPress installation will include an .htaccess file that you can access through your hosting control panel or FTP client. When you host multiple sites, your web server will also have multiple .htaccess files.
In this guide, you have learned how to locate the .htaccess files on your server. If the .htaccess files are not present for some reason, you need to manually create one and upload it to your server.
Need Expert Assistance?
Modifying server files can be intimidating. If you are a Gotmyhost customer and you’re worried about breaking your site configuration, our support team is available 24/7 to assist you. Whether it’s setting up a complex redirect or fixing a corrupted file, we’ve got your back.
Related topic: How to enable the .htaccess file on your web server