Meta Title: The Best Ways to Clone a WordPress Site for Testing and Development
Meta Description: Discover effective methods to clone a WordPress site for testing and development. Learn best practices to streamline your workflow. Read more now!
Cloning a WordPress site means creating an exact copy of the content, media, plugins, and database files. A clone WordPress site is a precise and stand-alone version that does not affect the original site. When cloning a site, the new site is completely decoupled from the original site, meaning changes to one will not impact the other.
Whether you are a developer, business owner, or site administrator, understanding how to clone a WordPress site is essential for safe testing, development, migration, and backup purposes. This guide explains how to clone a WordPress site, including all its content, media, plugins, themes, and database files. This guide covers manual, plugin-based, and managed hosting methods for cloning a WordPress site, ensuring you have the right approach for your needs.
The cloning process is invaluable for users who want to create a safe environment for testing purposes, such as experimenting with new features, plugins, or themes, without risking any changes to their live site.
For WooCommerce stores and other e-commerce websites, site cloning is especially important. It allows you to test updates, troubleshoot issues, and develop new features in a controlled setting before rolling them out to your customers.
By working on a cloned site, you can ensure your original site remains stable and uninterrupted while you innovate and improve it behind the scenes. Whether you’re a developer, business owner, or site administrator, the ability to create a duplicate site gives you the flexibility and confidence to make changes safely and efficiently.
Table Of Content
- Why Would You Clone a WordPress Site?
- Benefits of Cloning
- Safe Testing Environment
- Streamlined Development
- Preparing for the Cloning Process
- Backup Your WordPress Site
- Update Themes and Plugins
- Cloning Methods for WordPress Sites
- Choose a Suitable Cloning Method
- Method 1: Manual Cloning
- Method 2: Using WordPress Plugins
- Method 3: Using a Managed WordPress Hosting Service
- Choose a Suitable Cloning Method
- Cloning for Testing and Development
- Safe Testing Environment
- Backup and Fallback
- Creating Staging Sites
- Database Find and Replace
- Security Considerations
- Performance Optimization
- Optimizing Cloned Sites
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Common Questions People Ask
- Best Practices for Cloning
- Make A Smooth Clone Of Your WordPress Website
Why Would You Clone a WordPress Site?
Cloning your WordPress website is useful for several reasons.
First, cloning makes it simpler to switch hosting providers. You can just copy your site exactly as it is, including all content such as posts and pages, and move it to the new host without rebuilding anything.
Second, cloning is great for building a site on your local computer. This lets you work without publishing your site. Or you could copy a live website to your local device in order to experiment with new designs or plugins without hurting your live site. Cloning is also useful for testing purposes, allowing you to safely try out changes before applying them to your live site.
Third, you can clone any WordPress website to create a staging site. A staging site is a clone of your live website that’s kept online. Staging sites act as isolated environments for testing purposes, such as trying out server configurations, software upgrades, or code changes without affecting your live site. It lets you test updates or changes before visitors see them. When everything looks good, you push those changes live.
Benefits of Cloning
Cloning a WordPress site brings a host of benefits for website owners, developers, and businesses alike. By creating a duplicate site, you gain a safe environment to experiment and innovate without risking your original site. Whether you want to test new plugins, themes, or server configuration changes, a cloned site lets you do so with confidence, knowing your production site remains untouched.
Safe Testing Environment
A major advantage of cloning is the ability to set up a staging environment. This exact copy of your live site allows you to preview updates, troubleshoot issues, and refine features before rolling them out to your visitors. Using a reliable cloning tool, such as WPBlazer, you can quickly create a cloned site that mirrors your original site’s files, database, and settings. This process streamlines development, reduces downtime, and helps ensure a smooth transition when changes are ready to go live.
Streamlined Development
Cloning is also invaluable for larger sites or complex WordPress installations, where manual work can be time-consuming and error-prone. With the right tools, you can automate the process, saving time and minimizing the risk of mistakes. Ultimately, cloning empowers you to test, develop, and deploy with greater peace of mind.
Having established the benefits, let’s look at how to prepare your site for the cloning process.
You can read more on WordPress Errors as a reference.
Preparing for the Cloning Process
Before you begin cloning your WordPress site, there are a few steps you should take to ensure a smooth process:
First, always back up your website. You can use backup plugins to create a copy of your site, but it’s highly recommended to enable automatic backups. Automatic backups ensure your site is regularly saved, providing extra security in case anything goes wrong during the cloning process.
Make sure to update all themes and plugins to their latest versions. This helps prevent compatibility issues after cloning.
Remember, you may need to be logged into your hosting or plugin account to access backup and cloning features.
Backup Your WordPress Site
Creating a backup of your WordPress site is essential before making any changes to your site. This ensures that you have a restore point in case anything goes wrong during the cloning process. There are several backup plugins available for WordPress that make the backup process easy and automated. These plugins typically store your backups in a default folder or a location you specify, allowing you to organize your backup files efficiently. You can also delete old or unnecessary backups directly from the plugin interface to manage storage space. Choose a reliable backup solution and perform a full backup of your site.
Update Themes and Plugins
Make sure all your themes and plugins are updated to their latest versions. This helps prevent compatibility issues after cloning and ensures your cloned site runs smoothly.
Once you have completed these preparations, you can choose the cloning method that best fits your needs.
Cloning Methods for WordPress Sites
The plugin method for cloning a WordPress site is recommended due to its accessibility and ease of use. Plugins like Duplicator, All-in-One WP Migration, or hosting-level staging tools are recommended for duplicating a WordPress site.
Cloning a WordPress site can be done using a plugin-based method for simplicity or a manual method for complete control. Cloning a site can be done using various methods, including plugins and manual techniques.
Choose a Suitable Cloning Method
There are different methods available to clone any WordPress site, each with its own advantages and requirements. The plugin method is generally easier and recommended for most users, and many popular cloning plugins are available for free. Consider the following options:
Method 1: Manual Cloning
Manual cloning methods require technical expertise but provide more control over the process.
In this section, we’ll guide you through the steps involved in manually cloning a WordPress site. Before starting the manual cloning process, it is crucial to create a full backup of your website to prevent data loss.
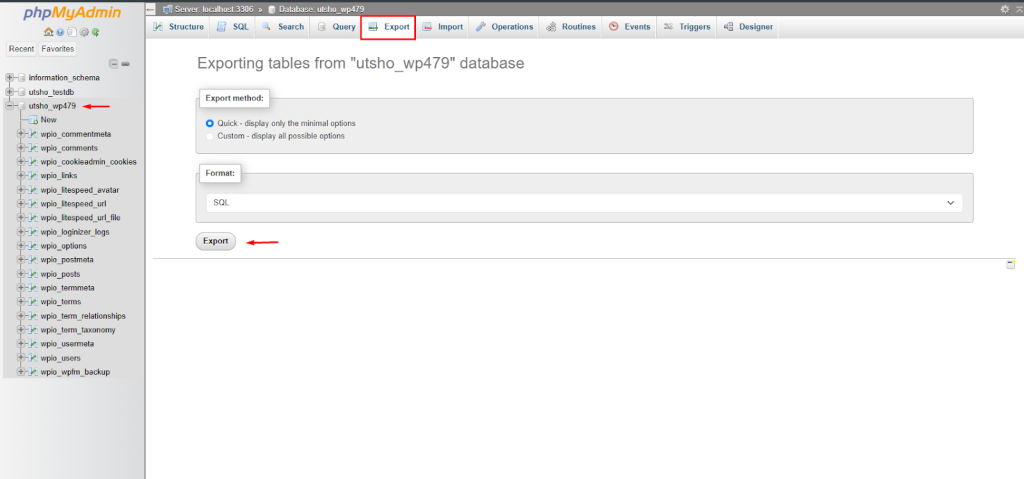
To begin, you need to export the database of your existing WordPress site. This is typically done via phpMyAdmin and is a necessary step for manual cloning. Export the database as an SQL file.
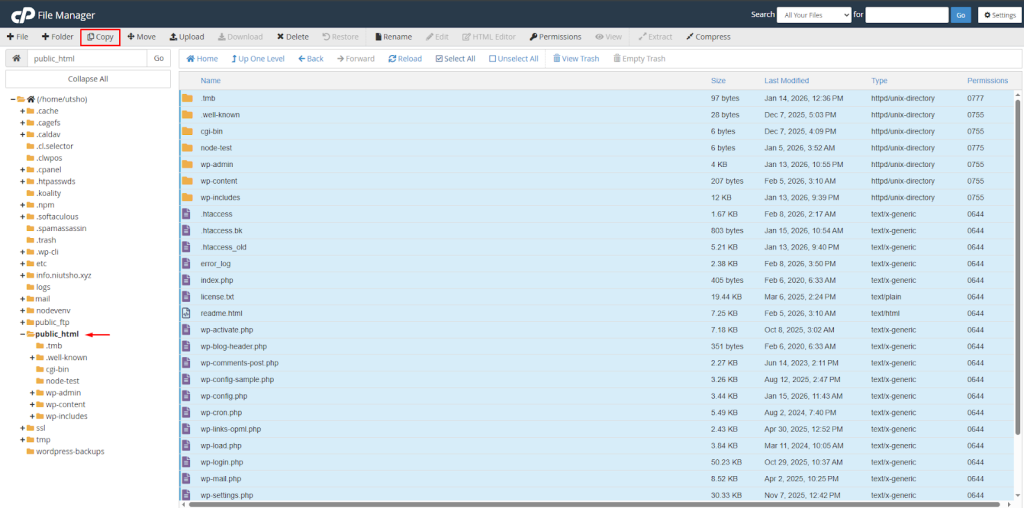
Next, you’ll need to copy all the files associated with your WordPress site. This includes the WordPress core files, themes, plugins, and any uploaded media files. Use FTP or a file manager provided by your hosting provider to download all WordPress files from the original site to your local computer. Pay special attention to the wp-content folder, as it contains your themes, plugins, and uploads. Backups created by some plugins may be stored in wp-content/uploads/wp-clone/.
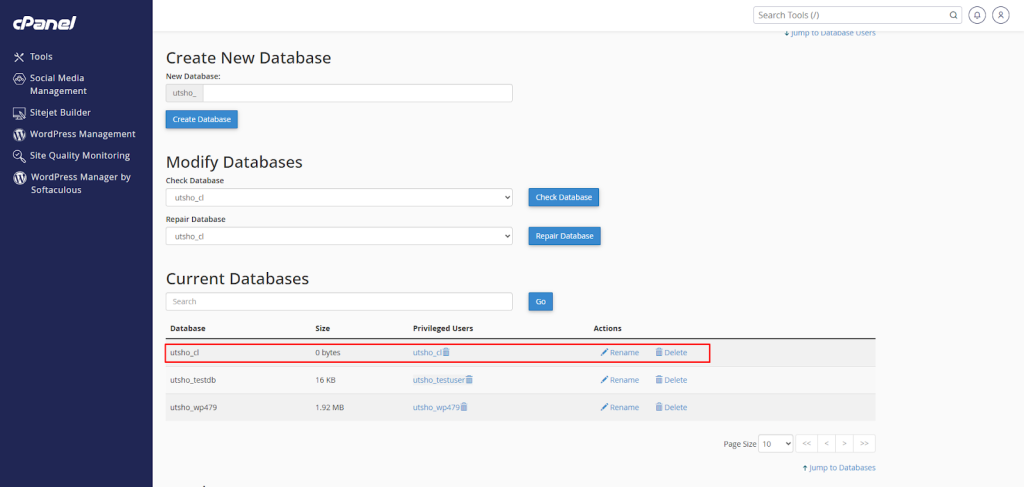
In this step, you’ll create a new MySQL database and user for your cloned site. Access your hosting control panel and find the database management section. Create a new database, a new user, and note down the database name, username, and password.
Now it’s time to import the exported database and upload the WordPress files to the new location. Import the SQL file into the newly created database using phpMyAdmin or the command line. Then, upload the WordPress files you copied earlier to the root directory of the new location, ensuring the wp-content folder is properly transferred.
In this final step, you need to update the configuration files to connect the cloned site to the new database. Locate the wp-config.php file in the root directory of the cloned site and open it in a text editor. You must manually update your database credentials (database name, username, and password) in wp config to match the new database you created. Save the changes to ensure your site connects to the correct database.
Congratulations! You have successfully cloned your WordPress site manually. Visit the new location in your web browser to verify if the clone is working correctly.
Manual cloning methods require technical expertise and can be time-consuming, especially when updating database records and configurations. However, they provide complete control and flexibility over the process, allowing you to safely test code changes in a staging environment before applying them to the live site. Some users prefer manual cloning for the control it offers, despite the additional effort required compared to plugin-based methods.
Transitioning from manual methods, let’s explore the more accessible plugin-based approach.
Method 2: Using WordPress Plugins
Plugin-based cloning methods offer convenience and speed for creating WordPress site copies and are generally easier and recommended for most users.
If you prefer a simpler and more automated approach, using WordPress plugins to clone your site is a great option—especially if you want to migrate your site or create a new site with minimal effort. Here’s how you can do it:
Log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to the “Plugins” section. Click on “Add New” and search for a cloning plugin like “Duplicator” or “All-in-One WP Migration”. Install and activate the plugin of your choice.
Popular plugins and their features include:
- Duplicator: Install it on the original site, create a package, and download the archive and installer files. Duplicator Pro packages the entire site into a zip file with an installer script for easy deployment.
- Migrate Guru: Handles migrations of large sites (up to 200 GB) by using external servers to prevent site crashes.
- All-in-One WP Migration: Features a simple drag-and-drop interface for exporting and importing entire sites.
- UpdraftClone: Creates instant cloud-based WordPress test environments with minimal effort and operates on a token system, where the number of tokens required depends on the size of the WordPress site. It also handles URL updates and secure hosting automatically.
- WPBlazer: The clone tool is easy to use and allows you to create a clone with just a few clicks.
- WP Clone: Allows you to create a backup that contains everything from your site, except the plugin’s own backups. Some plugins, like WP Clone, store backups in the default wp-content/uploads/wp-clone/ folder.
Once the plugin is activated, you’ll find a new menu item related to the plugin in your dashboard. Click on it to access the plugin settings. Configure the plugin according to your requirements, such as specifying the destination for the clone and customizing any advanced options if needed. Many plugins have default options for backup storage locations and copying data, but you can adjust these as needed. Make sure to follow the plugin’s documentation for specific instructions on configuring the plugin.
After configuring the plugin, you’re ready to initiate the cloning process. Depending on the plugin you’re using, you may need to follow different steps. Generally, you’ll find a “Clone” or “Create Clone” button within the plugin’s settings. Click on it to start the cloning process.
For example, with Duplicator, you would create a package on your original site, download the archive and installer files, and then upload them to your new site to complete the migration.
The plugin will handle the cloning process automatically, copying your site’s files, database, and settings to the specified destination. This may take some time, depending on the size of your site.
Once the cloning process is complete, the plugin will provide you with a link to access the cloned website. Visit the link to verify if the clone has been successfully created. After cloning, it is important to check that every page template, post, and form on the cloned website is functional to ensure everything works as expected.
Now that you know how to use plugins for cloning, let’s look at how managed WordPress hosting services can simplify the process even further.
Method 3: Using a Managed WordPress Hosting Service
If you’re using a managed WordPress hosting service, you need to be logged into your hosting account to access cloning and staging features. Many modern managed WordPress hosts, such as Pressable, WP Engine, and Kinsta, offer one-click cloning or staging environments for faster site duplication. Here’s how you can clone your site using such a service:
If you haven’t already, sign up for a managed WordPress hosting service that provides a cloning feature. There are various providers available, such as WP Engine, Flywheel, or Kinsta. Choose a provider based on your needs and budget.
Once you have signed up and logged in to your managed WordPress hosting dashboard (your account area), look for the cloning option. It might be listed as “Site Cloning” or “Copy Site” within the dashboard. Click on it to start the cloning process.
Follow the on-screen instructions provided by your hosting provider to clone your site. You may be able to set up the cloned site on a new domain, as a subfolder of your original domain, or even as another site in a multisite setup. During the cloning process, the system will automatically perform find-and-replace operations on the site’s database to update all records containing the site’s domain and path, ensuring the cloned site works seamlessly on the new domain or location.
WooCommerce stores and customer data are fully supported during the cloning process, so all customers, orders, and store information are preserved and transferred to the cloned site.
A cloned WordPress site is a precise, stand-alone version that is completely decoupled from the original site—changes made to one will not affect the other. For example, WP Staging creates a copy of your site in a subfolder for testing, updates, or development, allowing you to safely experiment without impacting your live site.
After the cloning process is complete, your managed WordPress hosting service will provide you with a link or temporary URL to access the cloned site. Visit the link and thoroughly test the cloned site to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
With your site successfully cloned, you can now use it for testing, development, or migration as needed.
Cloning for Testing and Development
For anyone managing a WordPress site, cloning is a cornerstone of effective testing and development. By creating a duplicate site, you can safely test new features, plugins, and themes without impacting your live site or production environment. This approach allows you to experiment freely, catch potential issues early, and ensure compatibility before making changes public.
Safe Testing Environment
A cloned site serves as a perfect staging ground for updates, letting you refine your work and verify everything functions as expected. If something goes wrong, you can troubleshoot and resolve problems in the staging environment, keeping your main site stable and accessible to users.
Backup and Fallback
Additionally, maintaining a backup clone of your site means you always have a fallback option in case of data loss or unexpected errors.
Whether you’re launching a new feature, updating plugins, or redesigning your site, cloning gives you the flexibility to test and perfect your work before it reaches your audience. This process not only protects your data but also enhances the overall quality and reliability of your WordPress site.
Next, let’s see how to create and use staging sites for even safer development.
Creating Staging Sites
Creating staging sites is a best practice for anyone managing a WordPress website. A staging site is a duplicate of your production site, designed specifically for testing and development. Using a cloning tool, such as WPBlazer, users can easily create a staging site in just a few clicks. The process typically involves selecting the original site you want to clone, entering the necessary details, and initiating the clone.
Once the staging site is created, it serves as a secure environment where you can test new plugins, themes, and code changes without any risk to your live site. This means you can experiment freely, troubleshoot issues, and perfect your updates before deploying them to your main website. Staging sites are especially useful for collaborative projects, as multiple users can work on the cloned site simultaneously, ensuring that all changes are thoroughly tested and reviewed. By integrating staging sites into your workflow, you can maintain the integrity of your production site while continuously improving your website’s features and performance.
Now that you understand the value of staging sites, let’s address how to update your database after cloning.
Database Find and Replace
After cloning your WordPress site, it’s crucial to update the WordPress database to reflect the new site’s URL and any other relevant information. This replacement process ensures that all links, media, and internal references point to the correct location on your cloned site, rather than the original site. Many cloning tools, such as WPBlazer, can automate this step, making the process faster and more accurate.
However, for larger sites, the find-and-replace process can be more complex, especially when dealing with serialized data in the database. Serialized data stores information in a specific format, and a simple search-and-replace can break this structure, leading to errors or lost data. That’s why it’s important to use a cloning tool that handles serialized data correctly.
If you’re working with a large WordPress database, be prepared for the process to take some time, and always test your cloned site thoroughly afterward. This helps ensure that all links, images, and features work as expected, and that your cloned site is a true reflection of the original.
With your database updated, let’s move on to important security considerations.
Security Considerations
When cloning a WordPress site, it’s essential to prioritize security throughout the cloning process. Since the process involves duplicating your site’s database—which may contain sensitive information like user accounts, passwords, and payment details—taking the right precautions is crucial. After creating a cloned site, users should immediately update the database credentials and modify the wp-config.php file to ensure the cloned site is not using the same access details as the original.
Additionally, it’s important to restrict access to the cloned site, especially if it’s being used as a staging environment. Consider password-protecting the staging site or limiting access to specific users to prevent unauthorized entry. By keeping the cloned site private, you reduce the risk of exposing sensitive data or unfinished features to the public. Following these security best practices helps ensure that both your original WordPress site and any cloned versions remain safe and secure throughout the entire process.
With security in mind, let’s look at how to keep your cloned site running efficiently.
Performance Optimization
Performance optimization is a key consideration when cloning a WordPress site, especially as the cloning process can result in a larger site with duplicate files and database entries. To maintain optimal performance, users should take proactive steps such as minimizing unnecessary database entries, optimizing images, and leveraging caching plugins to speed up the website.
Optimizing Cloned Sites
Using a tool like WPBlazer can further streamline the cloning process by allowing you to select only the essential files and database tables to be cloned, reducing bloat and improving efficiency. Regularly reviewing and cleaning up your WordPress files and plugins also helps keep your site running smoothly. By focusing on performance optimization during and after the cloning process, you ensure that both your original site and any cloned versions deliver a fast, seamless experience for your users and customers.
If you encounter any issues during the cloning process, the next section will help you troubleshoot common problems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
During the cloning process, you might encounter some common issues. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them:
- Database connection errors: If you experience database connection errors on the cloned site, double-check the database details in the configuration files or plugin settings. Make sure they match the new database you created for the clone.
- File permission issues: If you notice any file permission errors or missing files on the cloned site, ensure that the file permissions are set correctly. Consult your hosting provider’s documentation or support for guidance on setting proper file permissions.
- Broken links or missing content: If you encounter broken links or missing content on the cloned site, it could be due to incorrect URL references. Use a search and replace tool or a plugin specifically designed for updating URLs to update any references to the old site’s URL to the new site’s URL.
- Unexpected errors after cloning: If you encounter unexpected errors, review the code in your cloned site, especially if you made customizations. Issues in custom code can often cause problems that do not appear on the original site.
Remember, having automatic backups in place allows for quick recovery if troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue.
Common Questions People Ask
Here are the most frequent questions regarding WordPress site cloning, answered with simple explanations.
Does cloning a WordPress site require technical knowledge?
No, you can use various free WordPress plugins or managed WordPress hosting services that offer simple, user-friendly interfaces for cloning without technical expertise. These free plugins allow you to easily create a new site or clone your existing site with just a few clicks.
What is the difference between manual cloning and using plugins?
Plugins simplify the process with these default options; manual methods offer more flexibility and control over each step.
Are there any risks involved in the cloning process?
While cloning is generally safe, there are risks, such as data loss or compatibility issues. Enabling automatic backups can help prevent data loss by ensuring you always have a recent copy of your site before performing critical actions such as cloning or updating.
Can I clone a WordPress site to a different hosting provider?
Yes, you can clone any website to a different hosting provider using manual methods or plugins.
Best Practices for Cloning
To achieve a smooth and successful cloning process, it’s important to follow a few best practices. Always start by creating a full backup of your original site, so you have a restore point if anything goes wrong. Use a trusted cloning tool to handle the process, as this reduces the risk of errors and saves time.
After cloning, update your WordPress configuration file (wp-config.php) and any relevant PHP files to match the new site’s settings, including database credentials and server details. Make sure your cloned site uses a separate database from the original site to prevent data conflicts.
It’s also important to consider SEO implications. A cloned site can create duplicate content, which may affect your search engine rankings. To avoid this, set a canonical URL or add a noindex meta tag to the cloned site until it’s ready to go live. Finally, thoroughly test your cloned site to ensure all features, links, and plugins work as intended.
By following these best practices, you can confidently clone your WordPress site, minimize risks, and ensure a seamless experience for both you and your users.
Make A Smooth Clone Of Your WordPress Website
Cloning a WordPress site can be a valuable process for testing, development, and backup purposes. By following the step-by-step guide and choosing the appropriate method, you can easily clone your WordPress site and create replicas for various purposes. Whether you opt for manual cloning, using plugins, or leveraging managed WordPress hosting services, ensure that you test the cloned site thoroughly and update any necessary configurations to match the new environment. Cloning provides you with the flexibility to experiment, test, and safeguard your website effectively.